Website tracking is about to change forever! Google is set to ban third-party cookies from Chrome from next year. This will bring significant changes to how companies use cookies to track and monitor their target consumers. Website cookies have been an integral part of web browsing for many years, providing essential functionalities such as personalization and tracking capabilities. However, with the latest changes thanks to privacy concerns, regulatory shifts, and cutting-edge technologies, it’s time to ponder: what is the future of cookies? In this blog post, we will explore the future of website cookies and how to navigate a cookieless future.
The current state of website cookies
Understanding the current state of website cookies is essential to grasp their future implications. Website cookies are small text files stored on a user’s device, containing data related to their interactions with a website. They play a vital role in various aspects, such as session management, authentication, personalization, and targeted advertising.
These cookies come in different types, each serving distinct purposes. Session cookies are temporary and are deleted once the user closes their browser, ensuring privacy and limited tracking. On the other hand, persistent cookies have a longer lifespan, remaining on the user’s device to provide continuity across browsing sessions. Additionally, third-party cookies, which originate from domains other than the website the user is currently visiting, are commonly utilized for tracking and ad-targeting purposes. Understanding these variations sets the stage for anticipating the dynamic changes that lie ahead for website cookies.
Read more on cookies here.
Privacy Concerns and Regulatory Actions
In recent years, a tidal wave of privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), and Brazil’s Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), has reverberated through the digital landscape, profoundly impacting the use of cookies. These robust regulations strive to empower users with greater control over their personal data, necessitating websites to seek informed consent before storing or accessing cookies.
Moreover, a groundswell of awareness has surged among users regarding their online privacy. Concerns about data collection, storage, and usage by websites have intensified. This surging demand for privacy has ignited the need for transformative changes in how cookies are managed and utilized.
What is the future of cookies?
Google has announced that it will be phasing out third-party cookies in Chrome by the second half of 2024. This means that third-party cookies will no longer be able to track users across different websites.
Third-party cookies have been the primary way for advertisers to track users and target ads, and their removal will make it more difficult for advertisers to do this.
Google is not the only company that is phasing out third-party cookies. Apple has already blocked third-party cookies in Safari, and Firefox is planning to do the same in the future. This means that the online advertising industry will need to find new ways to track users and target ads in a cookieless world.
It is still too early to say what the future of cookies will look like. However, it is clear that you will need to adapt to a cookieless world. The industry will need to find new ways to track users and target ads, and it will also need to find ways to respect user privacy.
Impact of cookieless future
The cookieless future is fast approaching. As more and more browsers block third-party cookies, businesses and marketers are scrambling to find new ways to track and target users.
There are a number of alternatives to cookies that are gaining popularity. These include:
- Browser fingerprinting: This involves creating a unique identifier for each user based on their browser settings, hardware, and software.
- Local storage: This allows websites to store data on the user’s device.
- Session replay: This involves recording the user’s interactions with a website and then playing them back to track their behavior.
- Federated learning of cohorts: This is a technique that allows advertisers to group users together based on their interests. This information can then be used to target ads to groups of users, without tracking individual users.
These technologies offer a number of benefits, such as being more privacy-friendly than cookies. However, they also have some drawbacks, such as being less accurate and not as widely supported by browsers.
Here are some ways the lack of third-party cookies will impact the online world:
Role of first-party cookies
First-party cookies, which are set by the website the user is directly interacting with, will continue to play a significant role in the future. They are essential for website functionality and can be utilized for personalization while respecting user privacy.
First-party cookies remember login credentials, preferences, and shopping cart items, enhancing user interactions with websites. They enable personalization of content and advertising based on browsing history and interests, as well as collect analytics data for website improvement.
As the cookieless future approaches, first-party cookies will become more crucial for advertisers to track users and deliver relevant ads. They offer benefits such as privacy, personalization, and cost-effectiveness in reaching target audiences. Overall, first-party cookies are valuable tools for website owners and advertisers, becoming even more important in the cookieless landscape.
Impact of browser changes
Browser changes will have a significant impact on the use of cookies. Many browsers are phasing out support for third-party cookies, making it more challenging for advertisers to track users across different websites. Intelligent tracking prevention (ITP) initiatives are also being implemented to enhance user privacy by limiting the capabilities of cookies.
Use of first-party data
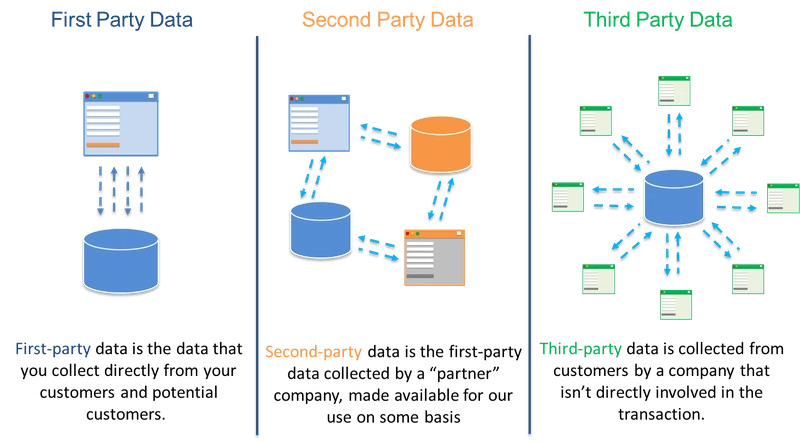
User-centric approaches to data collection will shift the focus from third-party data to first-party data. First-party data is the valuable information directly collected by a company from its customers. Due to its accuracy and reliability, first-party data holds numerous advantages for businesses. Companies can leverage this data to personalize marketing campaigns and enhance customer service. Using first-party data, businesses can make well-informed and strategic decisions to improve overall operations.
There are various channels through which companies can gather first-party data, including website tracking, email marketing, CRM systems, and social media interactions. This user-centric approach aims to empower individuals by giving them more control over their data and ensuring that their privacy is respected.
There is another type of information known as second-party data, which is the first-party data shared by a “business partner” to a company.
Rise of contextual advertising
Contextual advertising is set to become more prominent as third-party cookies diminish. This approach involves displaying ads relevant to the content a user is currently viewing on a webpage. It offers advantages like improved privacy and reduced reliance on user-specific data compared to behavioral targeting.
Contextual advertising analyzes webpage content to match ads, and its popularity is driven by the rise of ad blockers, growing privacy concerns, and advancements in technology. As the cookieless future approaches, contextual advertising is likely to gain more popularity due to its privacy-friendliness and effectiveness. While it has benefits such as being privacy-friendly, effective, and cost-effective, it also faces challenges in terms of complexity, accuracy, and the potential for spam. Nevertheless, contextual advertising shows promise in transforming the online advertising landscape.
In 2021, global contextual advertising spending was around $178.3 billion. It is projected to surpass $376.2 billion by 2027. The United States, with a market value of about $52 billion in 2020, holds the position of the largest contextual advertising market globally.
Role of AI and ML
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a crucial role in the future of website cookies. With the limitations imposed on third-party cookies, AI-powered algorithms can be utilized to personalize user experiences without relying heavily on cookies. These algorithms can analyze various data points, such as user behavior, preferences, and context, to deliver personalized content and recommendations. This approach not only enhances the user experience but also minimizes the reliance on intrusive tracking techniques.
Challenges of cookieless future
The future of website cookies comes with challenges, such as
- Impact on the digital advertising ecosystem: As third-party cookies are phased out, advertisers must adapt their strategies and find alternative ways to reach their target audience. Contextual advertising will gain importance, and advertisers will need to focus on delivering relevant ads based on the content and context of the user’s current session.
- Balancing personalization and privacy: While personalization is valuable for enhancing user experiences, it must be done in a privacy-conscious manner. Websites must prioritize user consent and ensure that they provide transparent information about data collection and utilization practices. Striking the right balance between personalization and privacy will be crucial to maintaining user trust and satisfaction.
- Less accurate targeting: Without third-party cookies, advertisers may have less accurate data about user behavior. This could make it more difficult to target ads to the right people.
- Reduced competition: As the cost of advertising increases, smaller businesses may be less able to compete with larger businesses that have more resources. This could lead to a decrease in competition in the digital advertising market.
Conclusion
As we navigate these changes, it is crucial for website owners, advertisers, and users to adapt and embrace responsible practices. Balancing personalization and privacy, ensuring user control and transparency, and upholding ethical standards will be key to creating a user-centric web experience. By embracing these changes and fostering responsible practices, we can build a future where website cookies play a valuable role in enhancing user experiences while respecting individual privacy.
Author bio: Roshan Philip is the founder and managing director of A&A Associate LLC. Additionally, he is a passionate writer and explorer, having contributed thousands of blogs and articles across the internet.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as legal or professional advice. The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of our organization. We do not endorse any products or services mentioned in the article.







