Blockchain technology is changing the way we do business. From sign-in data encryption and digital document validation to payment transactions, the uses of blockchain are limitless. Blockchain security is crucial, especially for those who rely on it daily. Despite using decentralized identifiers for added security (which allows users to create secure personas for different needs), cookies pose a significant threat. Did you know that a tracker can link a user’s Bitcoin transactions across sites using the same tracking cookies, revealing their identity? We’ll discuss this and more in the article.
How are cookies connected to blockchain security?
When users perform blockchain-based transactions online, cookies are generated by the website or the payment gateways. These cookies store information such as buyer characteristics (name, email, and physical address), items purchased, and time of purchase. Websites also use other information through cookies, such as transaction-specific wallet addresses.
Cookie-based data collection can have legitimate uses like retargeting, but it can also be used maliciously. Cookies can be used to link an identity to a blockchain account (cryptocurrency wallet or portal account). The blockchain transactions can then be used to reveal a person’s identity. Unintentional data leakage from cookies can also be combined with JavaScript to track a user’s system details.
Hackers can use multiple tracking cookies from various websites to gather details about their target. For instance, if a person uses two websites for online shopping and those sites use tracking cookies, then hackers could combine them. This would allow them to gather information about the person’s wallet address, email address, phone number, and name.
For example, a user named Alice made purchases on two different merchant sites and logged in on a third site, all of which use the same tracking cookies. The tracker obtained enough information to identify the Bitcoin transactions made by Alice and link them together based on her browser cookie.
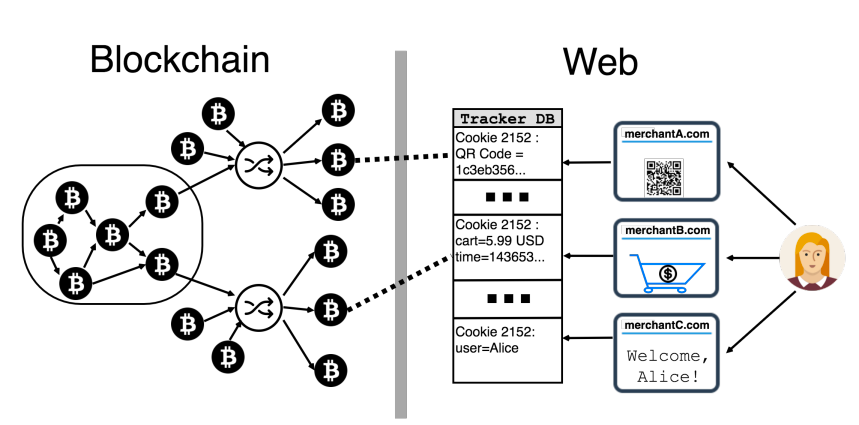
Although Alice had taken the precaution of using an anonymizing technique for her transactions, the fact that she used the same wallet for both transactions revealed her identity to the tracker. This demonstrates how even seemingly small pieces of information, like browser cookies, can be used to compromise the privacy and security of blockchain transactions.
Some websites use third-party APIs to generate information through fingerprinting, browser functions, and form sniffing. Tech giants such as Google and Facebook are known to tie their API tracking profile directly to a user’s real identity.
Even information that seems harmless can be used for malicious purposes. For example:
- Payment time: Cross-referencing the payment time with ledger documents can help identify the transacting account, which, in turn, enables the identification of user details through cookies.
- Sale price: Linking the user account to a geographical location is possible by using the sale price because the user’s wallet requires the exchange rate to convert their local currency to crypto. This allows a hacker to estimate roughly the user’s country of origin.
- Personal information: Hackers can use personal information such as payment address, email address, and shipping address to directly link a blockchain user to their account.
- Office phone number: Hackers can use the user’s office phone number to contact their mobile operator with fake identity proof and generate a duplicate SIM.
- Spending pattern: Hackers can use the spending patterns of users to carry out targeted scams against them, and they can also sell this information to advertising companies.
So how can you secure cookies?
There are several ways to secure cookies. For example, if you add the HttpOnly property to your cookies, JavaScript will not be able to access cookie data. This adds an extra layer of protection for your cookies and mitigates XSS attacks.
Website developers should also ensure that sensitive data (username, password, address and patent details) should have a shorter lifespan. Achieving this is possible through the use of the Expires attribute. You can set the time after which their cookie would be deleted by using the Max-Age tag. You can also ensure that data is encrypted before it is sent over a network (HTTPS) by using the secure attribute.
Additionally, you can use domains and paths to ensure that you transfer data only to trusted sources. Browsers also disable supercookies, which prevents man-in-the-middle attacks. Businesses can prevent cross-origin requests by using the SameSite attribute. This attribute ensures that data is only sent to the site from which it originated. By doing this, any cookie generated from your site will only be able to transfer information to your own site. The SameSite attribute’s value should be set to Strict.
Other ways to improve blockchain security
There are several other ways you can improve blockchain security.
Tracking protection browser tools, such as Adblock Plus and uBlock, can help protect user identity on the blockchain. You can also use mixing services to prevent hackers from tracking your transactions. Mixing services create a delay of 5-6 blocks per transaction, creating an anonymity set that confuses malicious hackers who try using your ledger transactions to link them to your identity.
You can also use a lightning network to create a bi-directional path between 2 parties without having it on the public blockchain ledger – making it safer than other methods. Some blockchain networks also bake security into their protocols, such as Zcash and Monero. But they are computationally expensive and difficult to maintain.
Lastly, simple steps, such as using HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP and using VPN, can also work wonders for your business. Yes, user privacy is a challenge, but following the above steps can greatly reduce the risk associated with blockchain.
Frequently asked questions
What is the role of cookies?
Cookies store small amounts of data on a user’s device that a website can access. This enables the website to remember user preferences, maintain user sessions, and personalize content. Additionally, cookies can serve tracking and advertising purposes.
What is the role of cookies in network security?
Cookies help improve network security by allowing websites to authenticate users and prevent unauthorized access. Additionally, cookies help in detecting and preventing phishing attacks by identifying and blocking suspicious requests.
What is the role of blockchain in security?
Blockchain technology can help improve security by providing a decentralized, tamper-proof record of transactions and data. This can help prevent fraud, hacking, and other security breaches by making it more difficult to compromise data.
Author bio: Chris is the Business Development Manager at BairesDev, responsible for enhancing relationships with customers, suppliers, and other partners. He is a skilled team leader, and his strategic planning abilities reach all areas of the business. His experience in sales, business, and technology enables him to write intriguing articles for BairesDev’s blog and other reputable media outlets. He has nearly 20 years of experience in the IT industry, working in various capacities.
Disclaimer: This article is for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as legal or professional advice. The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of our organization. We do not endorse any products or services mentioned in the article.